CPET 499/565 Mobile Computing Systems
Lecture Note 3
Smart Phones and OSs, Development Tools, Android
Application Framework
Professor Paul I-Hai Lin
Sept. 8,
2014
Mobile OS
· iPhone OS
· Android OS
· Windows Phone 8
· BlackBarry OS
iPhone OS Architecture
o iOS is a Unix based OS
o Based on proprietary Mach kernel and Darwin Core as Mac OS X
o BSD Unix
o File Systems
o I/O Systems
o Networking Components
o Main Features
o Home screen
o Folders
o Notification Center
o Default APPs
o Multitasking
o Switching Applications
o Game Center
Kernel Architecture Overview, https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/documentation/Darwin/Conceptual/KernelProgramming/Architecture/Architecture.html
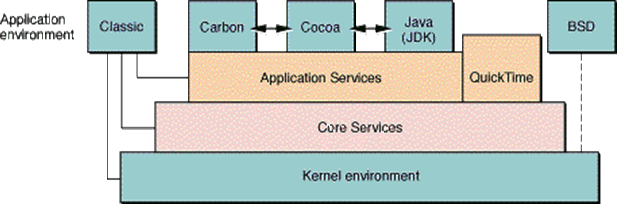
OS X Architecture
Microsoft Window Mobile OS
o Window Phone http://www.windowsphone.com/en-us
o What’s new in Windows Phone 8.1 http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/apps/dn632424.aspx
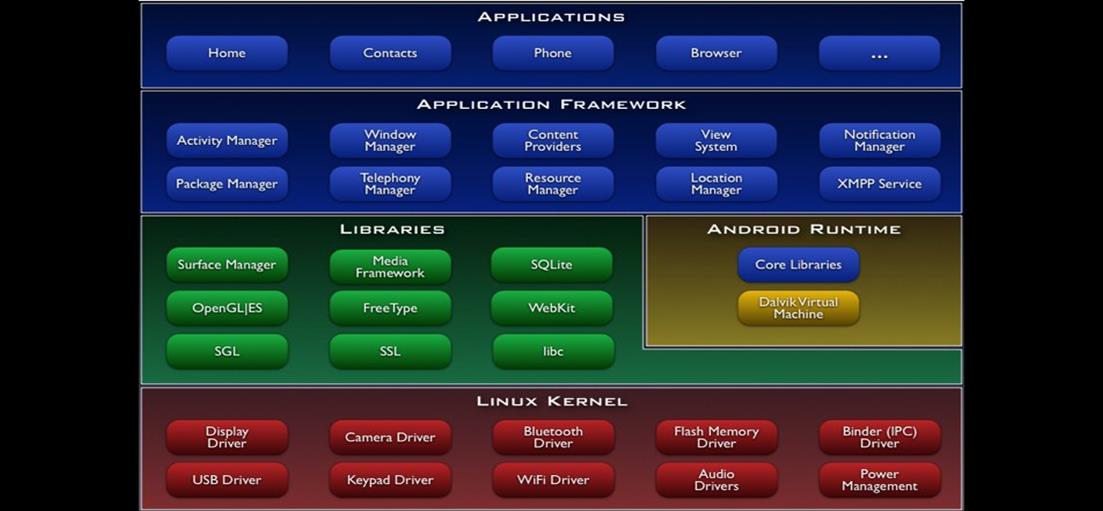
Android OS Architecture
· Created by Android Inc., as part of Google in 2005 for mobile devices: Tablets and Smartphone
· In 2007 Google formed an Open Handset Alliance with 86 hardware, software and telecom companies
· Development in Open Source – Source code is publicly available
· Developers are welcome to contribute via SDK
· Packages include Linux Kernel and Java-based application framework
o Linux Kernel – for core system services: security, memory management, and process management
o Runtime
§ Set of core libraries which supports Java functionality
§ The Dalvik Virtual Machine
§ Relying on Linux kernel for underlying functionalities such as threading …
· Libraries: C/C++ libraries
o Media libraries, system C library, surface manager, 3D libraries, SQLite, etc
· Application Framework
o An access layer to the framework APIs used by the core applications
o Allow components to be used by the developers
· Main Features
o Handset layouts
o Storage
o Connectivity – GSM/EDGE, CDMA, UMTS, Blouetooth, Wi-Fi, LTE, NFC, WiMax, etc
o Messaging – SMS, MMS, C2DM (Android Cloud to Device Messaging)
o Multiple language support
o Web browser
o Media support
o Streaming media support
o Additional hardware support
o Multi-touch
o Bluetooth
o Video calling
o Screen capture
o External storage
· Android OS Versions, http://developer.android.com/about/index.html
o 4.4 KitKat (2013), http://www.android.com/versions/kit-kat-4-4/
o 4.3 Jelly Bean, http://www.android.com/versions/jelly-bean-4-3/
o 4.2 Jelly Bean, http://www.android.com/versions/jelly-bean-4-2/
o 4.1 Jelly Bean (2012)
o 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich (2011)
o 3.0-3.2 – Honeycomb (2011)
o 2.3 – Gingerbread (2010)
o 2.2 – Froyo (2010)
o 2.0-2.1 – Éclair (2009 -)
o 1.6 – Donut (2009)
o 1.5 – Cupcake (2009)
References
· Android (Operating System), http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Android_(operating_system)
· Open Handset Alliance, http://www.openhandsetalliance.com/
o Android Open Source Project (Video), 2008, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Y4thikv-OM
· Mobile Operating System, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_operating_system
o Combines features of a typical personal computer’s OS with other features including:
§ Touchscreen, Cellular, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS mobile navigation, Camera, Video Camera, Speech recognition, Voice recorded, Music Player, Near field communication, Infrared blaster
· Introducing Android, http://www.android.com/about/
· List of Features in Android, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_features_in_Android
· Smartphone OS Showdown, by Sascha Segan, 2013/3/27, http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2417059,00.asp
· Smartphone OS Shootout: Android vs. iOS vs. Windows Phone, March 2011, http://www.computerworld.com/article/2506829/mobile-wireless/smartphone-os-shootout-android-vs-ios-vs-windows-phone.html
SmartPhone Hardwares and
Features
· 2014 Best Smartphone Reviews and Comparisons, http://cell-phones.toptenreviews.com/smartphones/
o Samsung Galaxy S5, Note
o HTC One
o LG G2, G Flex
o Apple iPhone
o Nokia Lumia
o Sony Xperia
o Google Nexus
·
Ratings:
Design, Camera, Battery Life, Internal Specs, Features, Carriers
o Design
§ Usability Score
§ Operating System
§ Screen Size (inches)
§ Display Resolution
§ Pixel Density (PPI)
§ Screen Technology
§ Weight
§ Dimensions
o Internal Specs
§ Processor Architecture: 32-bit, 64-bit (iPhone)
§ Processor Speed (GHz)
§ Number of Cores (2 or 4)
§ RAM (1, 2, or 3 GB)
§ Built-in Storage (16/32/64 GB)
§ Expandable Storage
o Features
§ 4G LTE
§ Telhering/Wi-Fi Hotspot
§ Bluetooth 4.0
§ Gyroscope
§ Compass
§ Accelerometer
§ Near Field Communication
§ Infrared Blaster
§ FM Radio
§ Fingerprint scanner
§ Water resistant
§ Included Headphones
References
· 2014 Best Smartphone Reviews and Comparisons, http://cell-phones.toptenreviews.com/smartphones/
· The Ten Best Smartphones, http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2367064,00.asp
Android Architecture
· Bootloader
· Boot Image
· System image
· Recovery image
· Radio image
Hardware
· MPU (MCU)
· RAM/ROM
· Screen
· Others
User Inputs
· Touch screen technologies
o Resistive
o Capacitive
o Surface acoustic wave
Sensors
· Accelerometer
· Magnetic field sensor
· Orientation sensor
· Temperature sensor
· Proximity sensor
· Light sensor
Sensors Overview, http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/sensors/sensors_overview.html
· Built-in Sensors for measuring Motion, Orientation, and various environmental condition
Development Tools
Mobile Devices – An Introduction to the Android Operating Environment Design, Architecture and Performance Implications, http://people.stfx.ca/x2011/x2011bhd/391/m_78_3.pdf
Android OS
· Android Open Source Project, http://source.android.com/
· Developers, http://developer.android.com/index.html
o Design, http://developer.android.com/design/index.html
o Develop, http://developer.android.com/develop/index.html
§ Android SDK download, http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
Android OS Major Components
· Android: A Complete Overview of Android OS Components, http://android.blogvasion.com/2012/12/android-complete-overview-of-android-os.html
Introduction to Android, http://developer.android.com/guide/index.html
Android Application Framework
· Provided in android.jar file
· Android SDK is made up of the following packages
|
Top-Level Package |
Purpose |
|
android.* |
Android application fundamentals |
|
dalvik.* |
Dalvik Virtual Machine support classes |
|
java.* |
Core classes and generic utilities for networking, security, math, etc |
|
javax.* |
Java extension classes: encryption support, parsers, SQL, etc |
|
junit.* |
Unit testing support |
|
org.apache.http.* |
HTTP protocol |
|
org.json |
JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) support |
|
org.w3c.dom |
W3C Java bindings for the Document Object Model core (XML and HTML) |
|
org.xml.sax.* |
Simple API for XML (SAX) support for XML |
|
org.xmlpull.* |
High-performance XML parsing |
· Android Application Framework FAQ, http://developer.android.com/guide/faq/framework.html
· Google APIs Add-On - an extension to the Android SDK, https://developers.google.com/android/add-ons/google-apis/
o The Maps external library
o The USB Open Access Library
o A sample Android application called MapsDemo
o Full Maps library documentation
· Android documentation references, http://developer.android.com/index.html
Application Fundamentals, http://developer.android.com/guide/components/fundamentals.html
· 4 types of app components
o Activities
§ An activity represents a single screen with user interface
· Email app
· Camera app
o Services (run on background)
o Content providers
§ Manage a shared set of app data
§ Each component is activated by an asynchronous message called “Intent”
§ The “Intent” can contain a Bundle of supporting information describing the component
o Broadcast receivers
Android App Components, http://developer.android.com/guide/components/fundamentals.html
· Activity, http://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/Activity.html
o public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper implements ComponentCallBacks …; http://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/Activity.html
o An android application is a collection of tasks, each of which is called an Activity
o An activity represents a single screen with a user interface
o Lifecycle: Getting created => Focused => Defocused => Destroyed
· Context, http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/Context.html
o
public
abstract class Context extends Object
o It allows access to application-specific resources and classes
o The central command center for an Android application-level operations such as
§ Launching activities
§ Broadcasting Intents
§ Receiving Intents
o All application specific functionality can be accessed through the Context
· Intent, http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/Intent.html
o
public
class Intent extends Object implements Parcelable Cloneable
o An abstract description of an operation to be performed.
o An Intent is recognized as a request to do something with late runtime binding between the code in different applications.
o The Android OS uses an asynchronous messaging mechanism to match task requests with the appropriate Activity
· Service, http://developer.android.com/guide/components/services.html
o An application component for performing long-running, background operations that do not provide a user interface.
o Tasks that do not require user interaction can be encapsulated in a service.
o Most useful when the operations are lengthy (offloading time consuming processing) or need to be done regularly (such as checking a server for new mail)
Performing Application Tasks
with Activities
§ Activity class, http://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/Activity.html
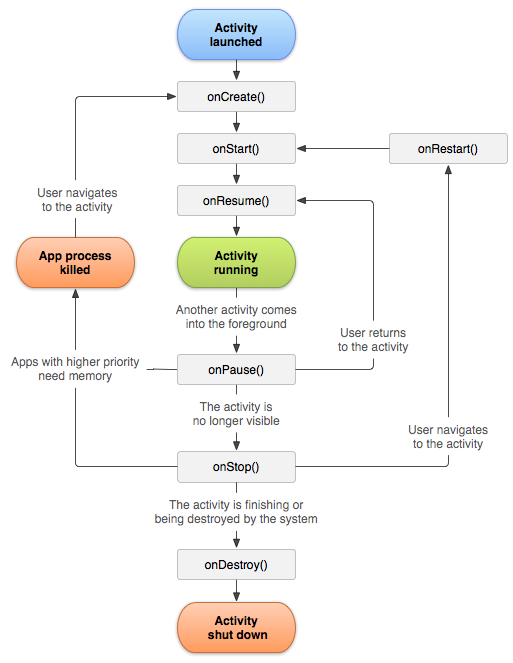
§ An Example – A simple game application might have the following 5 xActivities
o Startup/Splash Activity
§ Main Menu Activity
· Game Play Activity
· High Score Activity
· Help/About Activity
§ Lifecycle of an Android Activity
§ More Examples
o Using Activity Callbakcs to manage application state and resources
o Initializing static Activity data in onCreate()
o Initializing and retrieving Activity data in onResume()
o Stopping, saving, and releasing Activity data in onPause()
o Avoiding Activity objects being Killed
§ Under low-memory operation, OS can kill the process for any Activity that has been paused, stopped, or destroyed.
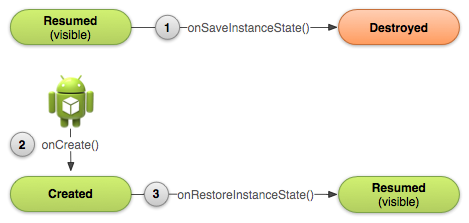
o Saving Activity state into a bundle with onSaveInstanceState()
o Destroy static Activity data in onDestroy()
Using Activity callbacks to
manage Application state and resources
Activities
· An activity specify an interaction with a user and is responsible for managing user interaction with a screen/window of information
· A window is automatically created with each activity
· Abstract class “Activity”
o OnCreate() method …. The entry point of an activity
o setContentView()
o onStart()
o onResume()
o onPause()
o onStop()
o onDestroy() … activity exits
· Using Activity Life Functions
o Screen orientation change
§ Destroy and recreate the activity from scratch
o Press home key
§ Pause the activity but does not destroy it
o Press application icon
§ Might start a new instance of the activity, even if the old one was not destroyed.
o Letting the screen sleep
§ Pause the activity
§ The screen awakening resume the activity
· Forcing Single Task Mode
o AndroidMainfest.xml
§ android:launchMode=”singleInstance”
§ android:launchMode=”singleTask”
· Forcing Screen Orientation
o Accelerometer sensor
o Portrait or landscape mode
§ android:screenOrientation=”portrait”
§ android:screenOrientation=”landscape”
o If you want to let the application handle orientation
§ android:configChanges=”orientation|keyboardHidden”
· Saving & Restoring Activity Info
o onSaveInstanceState()
· Multiple Activities
o Examples
§ Game has two activities: Game Screen and High-Score Screen
§ Notepad has three activities:
· View a list of notes
· Read a selected note
· Edit a selected or new note
o Using Buttons and TextView
o Launching a Second Activity from an Event
o Launching an Activity for a Result Using Speech to Text
o Implementing a List of Choices
o Using Implicit Intents for Creating an Activity
o Passing Primitive Data Types between Activities
Managing the Activity Life Cycle, http://developer.android.com/training/basics/activity-lifecycle/index.html
Starting
an Activity
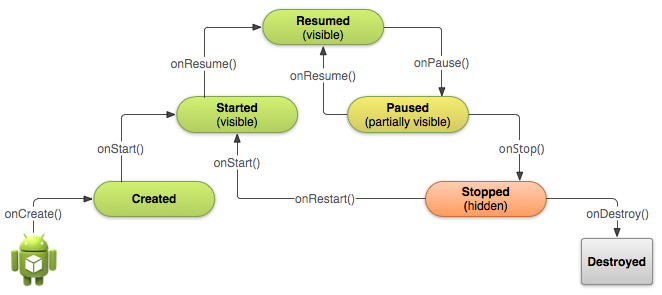
Pausing
and Resuming an Activity
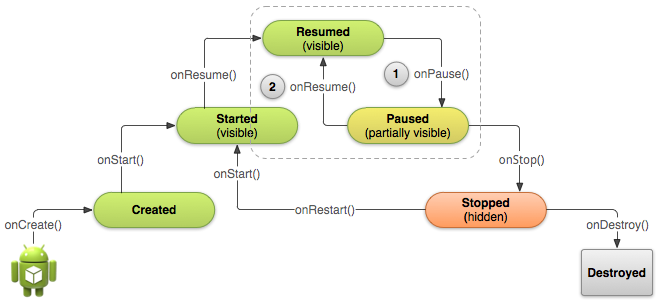
Stopping
and Restarting an Activity
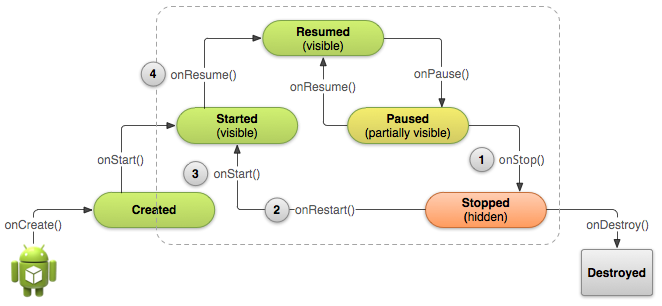
Recreating
an Activity
public class MyActivity extends Activity{
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState);
// Initialize static Activity data
protected void onStart();
protected void onRestart();
// Bring activity to Foreground
protected void onResume();
//Bring activity to Foreground
// Appropriate place for placing/starting Audio, Video, and Animators
protected void onPause();
// Pushed down the current Activity to the Activity Stack
// Should stop any Audio, Video, and Animators
//Deactivate resources such as a database Cursor object
//Last chance for clean-up any resources it does not needed while in the background
//Need to save any uncommitted data here, in case the application does not resume
protected void onStop();
protected voidonDestroy();
}
Using the Application Context
· Context class, http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/Context.html
· The application Context is the central location for all top-level application functionalities.
o Retrieving the Application Context
o Retrieving the Application Resources
o Accessing Application Preferences
o Accessing other Application Functionalities
§ Launch Activity instances
§ Retrieve assets packaged with the application
§ Request a system service (for example: a location service)
§ Manage private application files, directories, and databases
§ Inspect and enforce application permission
· public abstract class Context extends Object
o Inherited Methods from class: java.lang.Object
o Constants
o Public constructors – Context()
o Public Methods
§ getApplicationContext() method – retrieving the Application Context
§ getResources() method – retrieving Application Resources
§ getSharedPreferences() method – retrieve Application Preferences
§ ... etc
Managing Activity Transitions
with Intents
· public class Intent, http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/Intent.html
· Can be used with startActivity() to launch an Activity, and appropriate finish() methods
· Examples
o sendBroadcast(Intent intent) to send it to any interested BroadcastReceiver components
o startService(Intent) or bindServiceIIntent, ServiceConnection, int) to communicate with a background Service
· Other Examples
o Transitioning between Activities with Intents
o Launching a new Activity by class name
o Creating Intents with action and data (action/data pair)
o Launching an Activity belonging to another application
§ Customer Relationship Management (CRM) app
o Passing additional information using Intents
o Organizing Activities and Intents in an application using Menus
Launching an Activity belonging
to another application
· Customer Relationship Management (CRM) launch the Contacts application
o to browse the Contact database
o Choose a specific contact
o Return that contact’s unique ID
· Launch Phone_Dialer app with a specific number
Uri number = Uri.parse(tel:2604816339);
Intent dial = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DIAL, number)
startActivity(dial);
Intents List: Invoking Google applications on Android Devices (Target Application/Intent URI), http://developer.android.com/guide/appendix/g-app-intents.html
· Browser (view, web search)
· Dialer (call)
· Google Maps (view)
· Google Streetview
· etc
Working with Services
· Services, http://developer.android.com/guide/components/services.html
· An application component that can perform long-running operations in the background and does not provide a user interface
· Examples (Background processing/tasks)
o Handle network transactions
o Play music
o Perform file I/O
o Interact with content provider
· Launching two forms of services
o Started:
§ A service is “started” when an application component (such as an activity) starts it by calling startService() method, http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/Context.html#startService(android.content.Intent)
o Bound:
§ A service is “bound” when an application component binds to it by calling bindService()
· Other Examples of service implementations
o Routinely check updates: weather, email, or social network app
o A photo or Media app that keeps its data in SYNC online (package and upload new content in the background when the service is idle)
o A video-editing app might offload heavy processing to a queue on its service (to avoid affecting overall system performance for non-essential tasks)
Android Programming Exercises
· 1st Programming Exercise, Hello World, http://developer.android.com/training/basics/firstapp/index.html
· 2nd Programming Exercise, an Activity (a single screen with a text field and a button), http://developer.android.com/training/basics/firstapp/building-ui.html
· 3rd Programming Exercise, Starting Another Activity, http://developer.android.com/training/basics/firstapp/starting-activity.html
· 4th Programming Exercise, Managing the Activity Lifecycle, (download the activity demo), http://developer.android.com/training/basics/activity-lifecycle/index.html
o Starting an Activity, http://developer.android.com/training/basics/activity-lifecycle/starting.html
o Pausing and Resuming an Activity, http://developer.android.com/training/basics/activity-lifecycle/pausing.html
o Stopping and Restarting an Activity, http://developer.android.com/training/basics/activity-lifecycle/stopping.html
o Recreating an Activity, http://developer.android.com/training/basics/activity-lifecycle/recreating.html
References
[ 1] Android documentation references, http://developer.android.com/index.html
[ 2] Lauren Darcey and Shane Conder, Android Wireless Application Development, 2nd Edition, Addison Wesley, 2011
[ 3] Reto Meier, Professional Android 4 Application Development, 2012, John Wiley & Sons, Inc