TUTORIAL
COURSE
Java Computing
For
Distributed Industrial
Applications
Over the Internet
Presenter
Paul I-Hai Lin
Sponsored
by the
Industrial
Automation and Control Committee
of the
IEEE
Industry Applications Society
Ch 1.
Introduction to HTML for Web Page Design
World Wide Web
(an information system)
·
A global, interactive, dynamic, cross-platform, distributed,
graphical hypertext information system
·
A hypermedia system and hypertext system
·
The WWW information transfer protocol is called the
HyperText Transfer Protocol (http) which allows hypertext documents to be
transferred quickly between web browsers and servers
·
Web Browsers such as Netscape Navigator and Microsoft
Explorer are used by clients to get information from servers
·
W3C World Wide Web Consortium leads the support and defining
the languages and protocols that make up the Web (HTTP, HTML, etc)
·
Visit the Consortium’s home page at http://www.w3.org/.
URL
(Uniform Resource Locator)
-
A key concept in the operation of the World-Wide Web (WWW)
-
A compact representation of the location and access method
for a resource available via the internet
RFC 1738 defines URL formats for the following access schemes
-
file Host-specific
file names
-
ftp File
Transfer Protocol
-
gopher The
Gopher Protocol
-
http Hypertext Transfer
Protocol
-
mailto Electronic
mail address
-
news USENET
news
-
nntp USENET
news using NNTP access
-
prospero Prospero
Directory Service
-
telent Telnet
Protocol for Interactive sessions
-
wais Wide-Area
Information Servers
URL
Schemes
<scheme>:<scheme-specific-part>
Scheme Default Port Syntax
ftp 21
ftp://<user>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<cwd1>/<cwd2>/../<cwdN>/<name>;
type=<typecode>
http 80 http://<host>:<port>/<path>?<searchpart>
gopher 70 gogher://<host>:<port>/<selectror>
HTML (Hyper
Text Markup Language)
·
Tool for producing documents on World Wide Web
·
A language for mixing regular text with "markup"
tags for describing the text, document layout, contents, and linking to other
documents that stored on the WWW information system
·
HTML specifications can be found from the following sits:
·
http://www.w3.org/pub/WWW/TR/REC-htm132.html HTML
3.2
·
http://www.w3/org/TR/WD-html140/ HTML
4.0
·
http://www.w3.org/pub/WWW/TR/WD-frames Frames
·
http://developer.netscae.com/library/documentation/htmlguid/index Netscape
·
http://msdn.microsoft.com/workshop/author/newhtml Microsoft
- Web Site
for Web Authoring Tools
http://dir.yahoo.com/computers_and_internet/software/reviews/titles/internet/web_authoring_tools/
- Web
Browser Download Sites:
Netscape Navigator: http://home.netscape.com/download/
Microsoft Internet Explorer: http://www.microsoft.com/ie/download/
Sun HotJava: http://java.sun.com/products/hotjava/
IBM WebExplorer: http://www.networking.ibm.com/WebExplorer/
Web Pages
·
Each “Web Page” that we load from the web is a single
document, written in a language called HTML, that includes the text of its
document, its structure and any links to other documents, images, and other
media. In addition, some script languages can be used to create dynamic pages.
·
Web pages are normally organize with a combination of the
following organizations: hierarchy organization, linear organization, linear
with alternative, Web
·
Frames allow the document window to be divided into
rectangular regions, each associated with a separate HTML document
Publishing Web Pages (HTTP Server)
·
Install a computer and connected it to the Internet (TCP/IP
protocol support, IP address, and domain name) and running an HTTP server
·
The HTTP server takes the URL (Uniform Resource Locator, the
web address) specified by the client's browser and translates it into a
specific filename on the server's system
·
Create a "www" or "public_html"
directory for files
·
Create documents from remote system on the Internet and
upload files using FTP client
·
or working on the same HTTP server systems in the target
directory
·
Some commonly used defaults are: index.html, Welcome.html,
default.html
·
Notice that Microsoft uses "htm" extension as
default
·
Set file and directory permissions
·
Allows you to setup password access restrictions
·
Validate the documents using web wage validators
http://www.webtechs.com.html-val-svc/
http://ugweb.cs/ualberta.ca/~gerald/validate/
HTML Server
Support Tools
·
LiveWire from Netscape is an online development environment
for Web site management and client-server application development. It uses
JavaScript, Netscape's scripting language, to create server-based applications
similar to CGI programs.
·
Sun's Java Web server support a similar capability in Java
·
Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) support Active
Server Page for building dynamic documents
·
UNIX HTTP servers support "Server-Side Include"
Supporting
Sites:
Active Server Pages
http://www.microsoft.com/ntserver/web/default.asp
LiveWire
http://developer/netwscape/com/library/documentation/livewire
Microsoft: VBScript, JScript
http://msdn.microsoft.com/scripting/default.htm
Server Side Includes
http://hoohoo.ncsa.uiuc.edu/docs/tutorials/includes.html
Sun's Java Web Server
http://jserv.javasoft.com/index.html
The Basics
Structure of HTML Documents
·
HTML File types and extensions
ASCII Text: .txt
PostCript: .ps
GIF: .gif (Image file)
JPEG: .jpg .jpeg (Image
file)
AU Audio: .au
MPEG Video: .mpeg .mpg
·
Document Elements
·
Heading
·
Paragraph
·
Fonts, position
·
Bulleted List
·
Tables
·
Files (text, image file, sound file, video files)
·
Structure markup Tags (for overall document)
Begin
Tag End Tag
<HTML> </HTML>
<HEAD> </HEAD>
<BODY> </BODY>
<!-- This is a comment -- >
·
Tags for title
and heading
<TITLE> </TITLE> Title
<H1>
</H1> Heading 1
<H2>
</H2> Heading 2
…..……..
<H6>…</H6> Heading
6
·
Paragraphs
<p> … </p>
·
Link (Anchor)
<A> … </A>
HREF=”…” The
URL of the Hyper Text Reference document
NAME=” ..” The name of the anchor
·
Lists
<OL> </OL>
An Ordered (numbered) list
<UL> </UL> An
unordered (bulleted) liss
<MENU> </MENU> A menu list of items
<DIR> </DIR> A
directory listing
<LI > </LI> A
list item
<DL> </DL> A definition list or glossary list
<DT> A
definition term
<DD> The
correponding definition to a definition term
·
Character
Formatting
<B> </B> Boldface text
<I>
</I> Italic text
<HR> A
horizontal rule line
<BR> A
line break
<EM>
/EM> Emphasis
<STRONG>
</STRONG> Stronger
emphasis
<BLOCKQUOTE> </BLOCKQUOTE> Long
quotes
<CODE> </CODE> Code sample
<KBD> … <KBD> Text
to be typed
<VAR> …</VAR> A
variable
<SAMP> …</SAMP> Sample
text
<CITE>…</CITE> A
citation
<ADDRESS>…</ADDRESS> Signature of a author
<FONT> … </FONT> Change
Font size
SIZE=”…” from 1 to 7
·
Tables
<TABLE> …</TABLE> Create a table
<CAPTION> …</CAPTION> Caption of table
<TR>…</TR> A
table row
<TH>…</TH> A
table heading cell
<TD>…</TD> A
table data cell
·
Images
<IMG>
SRC=”…” Insert an inline
image into the document
·
Forms
<FORM> …</FORM> Indicates
a form
<INPUT> An
input widget for a form
<TEXTAREA> …</TEXTAREA>
<SELECT> …</SELECT>
<OPTION>…<OPTION>
HTML Scripting
for Dynamic Documents
·
JavaScript from Netscape
·
JScript from Microsoft
·
VBScript uses syntax more familiar to Visual Basic programmers
·
Java Applets
·
ActiveX control embedding: label, pop menu, HTML pop window,
URL preloader, timer, etc
Some
HTML Web Page Examples
A Tic-Toc-Toe Table Example
<!TicTocToe.html ->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>A Tic Toc Toe Table Example</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<CENTER>
<TABLE BORDER=1
FRAME="VOID">
<TR><TH>X<TH>O<TH>X
<TR><TH>X<TH>O<TH>X
<TR><TH>O<TH>X<TH>O
</TABLE>
</CENTER>
</BODY>
</HTML>
An
Example of Writing Equations
<!Equations.html-->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Equations with Superscripts and
Subscripts</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY
BGCOLOR="WHITE">
<H1>Character
Styles</H1>
<U>Underlined</U><BR>
<STRIKE>Underline</STRIKE><BR>
Subscripts:
v = v<SUB>0</SUB> + v<SUB>1</SUB> +
v<SUB>3</SUB><BR>
Superscripts:
x<SUP>2</SUP> + y<SUP>2</SUP> + z<SUP>2</SUP><BR>
</BODY>
</HTML>
A
Serach Engine Example
<!SEngine.html-->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>My Search Engines</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1>My
Search Engines</H1>
Try
one of the search engines below for connecting
to
other popular search sites:
<P>
<TABLE
BORDER=1>
<TR
BGCOLOR="RED"><TD><FORM
ACTION="http://www.altavista.com/">
<INPUT TYPE="SUBMIT"
VALUE="AltaVista">
</FORM>
<TD><FORM
ACTION="http://www.excite.com/">
<INPUT TYPE="SUBMIT"
VALUE="eXcite">
</FORM>
<TD><FORM
ACTION="http://www.hotbot.com/">
<INPUT TYPE="SUBMIT"
VALUE="HotBot">
</FORM>
<TR
BGCOLOR="BLUE"><TD><FORM
ACTION="http://www.infoseek.com/">
<INPUT TYPE="SUBMIT"
VALUE="InfoSeek">
</FORM>
<TD><FORM
ACTION="http://www.lycos.com/">
<INPUT TYPE="SUBMIT"
VALUE="Lycos">
</FORM>
<TD><FORM
ACTION="http://www.yahoo.com/">
<INPUT TYPE="SUBMIT"
VALUE="Yahoo">
</FORM>
</TABLE>
</BODY>
</HTML>
A
Multiple Frame Example
<!--
FrameTableCont.html -->
<!--
Top Level HTML file -->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>IEEE IAS Industrial Automation
and Control</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<FRAMESET
ROWS="100,*">
<FRAME SRC="Topics.html"
NAME="TOPICS">
<FRAME SRC="IntroIACC.html"
NAME="Main">
<NOFRAMES>
<BODY>
For a non-Frames version, do this
<A
HREF="IntroIACC.html">the introduction</A>.
</BODY>
</NOFRAMES>
</FRAMESET>
</HTML>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
<!IntroIACC.html
-->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>IAS MSDAD IAC
Committee</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1>Institute
of Electrical and Electronics Engineers </H1><BR>
<H2>Manufacturing
Systems Development and Applications Department (MSDAD)</H2><BR>
<H3>- Appliance Industry
Committee<BR>
- Electrostatic Process
Committee<BR>
- Industrial Automation and Control
Committee<BR>
- Production and Applications of
Light Committee</H3><BR>
</BODY>
</HTML>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
<!Officers.html
-->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Industrial Automation and
Control Committee</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1> Officers of IACC </H1>
<H2>
Chairman: Muhammad H. rashid<BR>
Vice Chairman: Ahmed Rubaai<BR>
Secretary: Takoi Hamrita<BR>
Past Chairman: Donald S. Zinger<BR>
</H2>
</BODY>
</HTML>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
<!Scope.html
-->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Industrial Automation and
Control Committee</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1> Scopes of IACC </H1>
<H2>
The Industrial Automation and Control
Committee is responsible for all metters
within the scope of the IAS in which
the emphasis or dominant factor specifically
relates to the applications of
industrial electrical and electronics devices, systems
and methods to the conversion,
regulation and utilization of electricity for the
control of industrial processes,
machinery and heating.
</H2>
</BODY>
</HTML>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
<!Subcommittees.html
-->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Industrial Automation and
Control Committee</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1> Subcommittees of
IACC </H1>
<H2>
Executive Subcommittee: Chairman -
Muhammad H. rashid<BR>
Electric Process Heating
Subcommittee: Chairman - Adam
Skorek<BR>
Papers Review and Prize Awards
Sucommittee: Chairman- Ahmed Rubaai<BR>
Standards Subcommittee: Chairman -
Ashfag Ahmed<BR>
</H2>
</BODY>
</HTML>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Embedded
JavaScript
<!--
hiieee.html -->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<BODY
BGCOLOR=WHITE>
<TITLE> FIRST JAVASCRIPT
EXAMPLE </TITLE>
<H1>
<SCRIPT LANGUAGE=JAVASCRIPT
TYPE="TEXT/JAVASCRIPT">
document.write("Hello
IEEE Members!")
</SCRIPT>
</H1>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Embedded
Java Applet Programs
The
APPLET tage enables us to embed a Java program into a page and send over to
client computer.
<APPLET
CODE="…"
WIDTH= xxxx
HEIGHT=xxxx ….>
</APPLET>
Embedding ActiveX Controls
<OBJECT
CLASSID="clsid: …"
WIDTH = xxx
HEIGHT = xxx
VPAGE = 0
ALIGN="LEFT"
>
Ch 2.
Networking Transport and Internetworking Layers
TCP
(Transmission Control Protocol)
·
Peer-to-peer transport protocol
·
A connection oriented protocol that provides a reliable,
full-duplex byte stream for a user process.
·
Since TCP uses IP, the entire Internet protocol suite is
often called the TCP/IP protocol family.
·
Some computational overhead that might affect throughput
·
Transport layer duties:
o
End-to-end delivery (treat individual packets independently)
o
Addressing (many-to-many entities called service points)
o
Reliable delivery (error control, sequence control, loss
control, and duplication control)
o
Flow control
o
Multiplexing
TCP
Segment Format
- Source
port address (16-bit)
- Destination
port address (16-bit)
- Sequence
number (32-bit): shows the position of the data in the original data
stream
- Acknowledge
number (32-bit)
- Header
Length (4-bit): number of 32-bit word in the header
- Reserved
(6-bit)
- Control
(6-bit)
- URG:
Urgent pointer field is valid
- ACK:
Acknowledgement field is valid
- PSH: Push
flag, pass this segment immediately for high throughput
- RST:
Reset flag is used when all else fails
- SYN:
Synchronized flag is used at the beginning of connection setup between two
nodes
- FIN: Terminate connections
- Window
Size (16-bit): Buffer space allocated for the connection
- Checksum
(16-bit): On header and data
- Urgent
Pointer (16-bit): Points to the end of data in the data field that is
considered as urgent and required immediate attention
- Options:
Variable length, Maximum Segment Size (MMS) could be sent
- Padding:
Padding on a 32-bit boundary, so that the data offset may correctly point
to it
UDP
(User Datagram Protocol)
- Also
called datagram service (regular mail service)
- A
connectionless protocol for user processes
- There is
no guarantee of delivery
- Provide
only simple functions:
- Can
discover errors
- No
sequencing function
- No
reordering function
- Cannot
specify the damaged packet when reporting errors
- UDP
Support Protocols
- Internet
Name Server Protocol (INSP)
- Possible
UDP Applications
- Broadcast
or multicast services
- Real-time
data (video, audio, industrial control, etc)
- Short
transaction time that assume implicit acknowledgement and tolerance on
duplicate datagrams
UDP
Datagram Format
- UDP
Header: 8-Byte Header + Data (variable up to 64K)
- Fields of
Header:
- Source
port address (16-bit)
- Destination
port address (16-bit)
- Total
length (16-bit)
- Checksum
(16-bit) for error detection
Ports
- 16-bit
port address, fixed binding
- Both UDP
and TCP use port addressing to deliver information
- Well-known
port (reserved)
- Port
number from 1024 and below
- Port
number between 1024 and 5000 are usually for custom servers
Port
Mapper
NFS uses this dynamic alternative
service
Allows new port to be defined and
registered dynamically
The
Service File
- The
Service File (Port Translation): a flat file database
- The
Internet Request for Comment RFC 1060 defines the file format
- A partial
listing of a common service file:
apollo% cat
/etc/services
#ident "@(#)services 1.16 97/05/12
SMI" /* SVr4.0 1.8 */
#
# Network
services, Internet style
#
# <service
name> <port number>/<protocol> [aliases ..] [#<comment>]
tcpmux 1/tcp
echo 7/tcp
echo 7/udp
discard 9/tcp sink null
discard 9/udp sink null
The
Service File (continue)
systat 11/tcp users
daytime 13/tcp
daytime 13/udp
netstat 15/tcp
chargen 19/tcp ttytst source
chargen 19/udp ttytst source
ftp-data 20/tcp
ftp 21/tcp
telnet 23/tcp
smtp 25/tcp mail
time 37/tcp timserver
time 37/udp timserver
name 42/udp nameserver
whois 43/tcp nicname #
usually to sri-nic
domain 53/udp
domain 53/udp
domain 53/tcp
bootps 67/udp #
BOOTP/DHCP server
bootpc 68/udp # BOOTP/DHCP client
hostnames 101/tcp hostname #
usually to sri-nic
sunrpc 111/udp rpcbind
sunrpc 111/tcp rpcbind
#
A
Comparison of IP, UDP and TCP
IP UDP TCP
Connection-Oriented?
no no yes
Message boundaries?
yes yes no
Data checksum?
no opt. yes
Positive Ack?
no no yes
Timeout and rexmit?
no no yes
Duplicate detection?
no no yes
Sequencing?
no no yes
Flow Control?
no no yes
TCP
In Action
- Two hosts:
149.169.1.0 à
149.169.1.9
- The
Connection Setup Phase
- SYN Flag
Set; Ack Flag (Not Set) -- Initial segment
- SEQ_No
Value 821
- The Data
Sending Phase
- The Final
Phase
Check the Status of Server for Measurement and Control
C:\>ping
149.164.36.20
Pinging 149.164.36.20
with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from
149.164.36.20: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=64
Reply from
149.164.36.20: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=64
Reply from
149.164.36.20: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=64
Reply from
149.164.36.20: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=64
Ping statistics for
149.164.36.20:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0
(0% loss),
Approximate round
trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 2ms, Average = 1ms
C:\>
Ch 3.
Java Programming
Language
Features of Java
- Secure -
virus-free, tamper-free
- Robust -
not memory overwrite
- Portable
- run on different machine without change
Java Components
·
The Java compiler - translate Java code to byte code
·
The Java interpreter - reading and executing Java byte code
·
The applet viewer
Byte
Code - A highly portable machine language for an imaginary Java computer
Java
Virtual Machine (JVM) - a computer that runs Java byte code
Just-In-Time
(JIT) compilation - some JVM can translate byte code into machine language
Java Programs
·
Java stand alone
applications (console or window-based)
- Java
applets
Java
Technology Tools and Download Sites
- Sun Java
- Microsoft
Visual J++
- Symentic.com
- Borland
Jbuilder
- IBM
VisualAge
SUN
Java http://java.sun.com/
Microsoft http://www.microsoft.com/java
MAC
OS http://applejava.apple.com/
IBM http://www.ibm.com/Java/tools/jdk.html
Microsoft
Windows Foundation Classes application
Java
Foundation Classes (JFC)
Multithread
applications
Java
COM (Component Object Model)
Java
Applications
-
Network programming (java.net)
-
Applet for dynamic Hypertext Markup Language document (java.Applet)
-
Graphical User Interface
Stand-Alone
Programs
- Programs
that runs on the computer in the same manner as any other window-based
application
Java
applet
- Small
Java programs that run in a JVM and is incorporated into a Web Browser
- An applet
runs inside a Web browser or an applet viewer
- An applet
cannot manipulate the computer file system
- An applet
is launched from HTML page
- Java
class extends java.applet.Applet
- Defined
in the java.awt package
Java Beans
- JavaSoft
Definition: “A Java Bean is a reusable software component that can be
manipulated visually in a builder tool.”
- For
building GUI-intensive applications similar to Visual Basic and Delphi
environment through control objects
- Needs to
implement Serializable interface for maintaining persistence
Java Native Methods
- Mixed-language
solution (not 100% pure Java)
- Support
only calling a C/C++ function (native code) from Java
- The needs
- Reuse
C/C++ functions or codes
- Access
system features or devices (such as serial port, digital I/O devices,
etc.)
- Maximize
code execution speed
- Disadvantages
- Losing
program portability
Some
Java Class Libraries
Applet
Class
java.applet.Applet
Networking
Classes
java.net.*
java.net.URL
java.net.URLConnection
java.net.DatagramSocket
The
Math class
Math.abs(aNumber), Math.exp(double), Math.log(double),
Math.max(double, double), Math.max(float, float), Math.max(long, long), Math.max(int, int), Math.min(double,
double), Math.pow(double, double),
Math.random(), Math.round(double), Math.sin(double), Math.cos(double), Math.tan(double)
Vector
Class
import java.util.*;
void addElement(Object obj)
boolean contains(Object obj)
Object elementAt(int index)
int indexOf(Object obj)
void insertElementAt(Object obj, int index)
boolean isEmpty()
void removeElement(Object obj)
void removeElementAt(int index)
void setElementAt(Object obj, int index)
int size()
The
Graphics Class
import java.awt.*;
drawLine(), drawRect(), drawOval(), drawArc(),
drawPolygon(), drawRoundRect(), drawString()
The
File Classes
import java.io.*;
FileInputStream,
FileOutputStream Classes
File tempfile = new File("tempdata.dat");
File voltfile = new File("voltdata.dat");
File ampfile = new File("ampdata.dat");
boolean canRead() - if
a file redable
boolean canWrite() -
if a file writeable
boolean exits() - if
a file exists
String getname() -
gets the file's name
String getPath() -
gets the file's path
String getParent() -
gets the folder's name
long length() -
gets the file's size
long lastModified() - gets the last update time
DataInputStream,
DataOutputStream Classes
char readChar()
double readDouble()
int readInt()
String readUTF()
void writeChar(char ch)
void writeDouble(double d)
void writeInt(int I)
void writeUTF( String s)
Terminal
Input and Output
System.err().println()
System.out().println()
FileDialog
Class
FileDialog(Frame parent, String title, int type)
String getFile()
String getDirectory()
void setSize(int width, int height)
setVisible(boolean flag)
new File(<directory>, <fileName>)
Java
Reserved Keywords
abstract boolean break byte case
catch char class const continue
default do double else extends
final finally float for future
generic goto if implements import
inner instanceof int interface long
native new operator outer package
private protected public rest return
short static super switch synchronized
this throw throws transient try
var void volatile while
Data
Types
Booleans
- TRUE, FALSE
Characters - char
Integer - byte, short, int, long
Float - float, double
String - array of characters
Java
Operators
Operation Symbol
Grouping ( )
Methods
selection .
Unary
minus -
Unary
plus +
Increment ++
Decrement --
Multiplication *
Division /
Remainder %
Addition +
Subtraction -
Equal ==
Not
equal !=
Less
than <
Less
than or equal <=
Greater
than >
Greater
than or equal >=
Assignment =
Add
and assign +=
Sub
and assign -=
Multiply
and assign *=
Div
and assign /=
Remain
and assign %=
Logical
Operators
AND &&
OR ||
NOT !
Variables
Types and Naming Conventions
Case
sensitive
Constants
Class
constant: combining final and static
static final private int MIN = 0;
static final private int MAX = 10000;
Control
Statements
if(condition){
statements;
}
if(condition){
statements;
}
else{
statements;
}
for(statement1;
condition; statement2)
{ block statement;}
do{
statements
} while(condition);
switch(expression){
case 1:
statements;
break;
case 2:
statements;
break;
…….
case n:
statements;
break;
default:
statements;
break;
}
Java
Object-Oriented Programming
Class
- public
methods (interfaces) as seen by clients
- Internal
implementation
Class
Inheritance
- Reusing
codes
- Classes
inherits the instance variables and methods of the classes above them in
the hierarchy
- A class
can extend its inherited characteristics by adding instance variables and
methods
- A class
can extend its inherited characteristics by overriding inherited methods
Abstract
Class
- Classes
that must never be instantiated in a hierarchy
- For
defining features and behavior common to their subclasses
- In Java,
the class Object is at the base or root of Java’s class hierarchy
Protected
Method
When
a method should be visible to subclass but not to the rest of the system
Abstract
Method
A
method abstract (in an
abstract class) when that method must be implemented by all subclasses
Final
Method
Declare
a method final when that method should be inherited but not overridden by
any subclass
Super
Method
When
overriding a super-class method, use that super-class method (super)
Methods
main()
JVM
sends the message main() to a program object
Execution
of the method main()
Some
Examples:
abstract public class Sensor extends Object{
….
}
public class TempSensor extends Sensor{
….
}
public class VoltageSensor extends Sensor{
….
}
public class CurrentSensor extends Sensor{
….
}
Possible
Member Functions:
Location()
Calibrate()
SetMaxVolt()
SetMaxAmp()
InitVoltSen()
InitAmpSen()
InitTempSen()
ReadVoltl()
ReadAmp()
ReadTemp()
Declare
An Array of Sensors
// declare an array variable
TempSensor[] TempSensors;
// Reserve space for 10 sensors
TempSensors = new TempSensor[10];
The Tools and Resources Used in Java Programming
- Editor à MyProg.java
- Compiler
(MyProg.java + Java Libraries) à MyProg.class
- Run
(MyProg.Java + Java Libraries + User Input)
Some common development environments
- UNIX -
using standard text editor and the command line
- Windows9x
- using Notepad for the editor and the command line
Programming Errors
- Syntax
error - violation of language syntax rule
- Run-Time
Errors - illegal operations, div by zero
- Logic
Errors - designing errors or bugs
Debugging
Print execution values - System.out,printlin()
Getting
Started with Java
- Install
Java
- Install a
Java-Enabled Browser
- Create
and run a Java Program
Simple
Standalone Java Examples
//
jaHello.java
// 1.
Edit the program using the Notepad
// 2.
Open MS-DOS Window
// 3.
Set path=c:\devstudio\sharedide\bin
// 4.
Compile jvc jahello.java
// 5.
Execute c:\windows\jview jahello.class
// 6.
Using SUN Java
// c:\jdk.1.2.1\bin\javac jaHello.java .... case sensitive
// c:\jdk.1.2.1\bin\java jaHello.class
import
java.lang.System;
public
class jaHello{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello IEEE
Industry Application Society");
}
}
Simple
Java Applet Examples
//
WebHello.java
// This
is a Java Applet.
// No
main() method in an applet program.
//
// 1.
Edit the program and name it -->
WebHello.java
// 2.
Compile the program to get -->
WebHello.class
// 3.
Prepare a HTML file that uses the APPLET -->
WebHello.html
import
java.awt.*;
import
java.applet.*;
public
class WebHello extends Applet {
public void paint(Graphics g) {
g.setFont(new
Font("TimesRoman",Font.BOLD+Font.ITALIC,30));
g.setColor(Color.red);
g.drawString("IEEE Industry
Applications Society!",50,800);
}
}
<!--
WebHello.html -->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>A Java
Applet</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY
BGCOLOR="white">
<APPLET
CODE="WebHello.class" WIDTH=750 HEIGHT=200>
[WebHello applet]
<!-- For non-Java Browser -->
</APPLET>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Ch 4.
Java Network
Programming
Network Client
- Actively forms a connection to a computer,
printer, etc., on the network
- Have a network address (dynamic or static)
Network Server
- Connected to a network continuously and wait for
a client to connect to it and provide services
- Has a static network address
Distributed Client/Server Applications
- Point-to-point connection
- Identified as a <host, socket> pair
Network Support Classes
The java.net library contains the
following classes for networking support
·
Web HTTP support
classes: InetAddress , URL, URLConnection,
HttpURLConnection
- Client-side networking support: Socket, and
InetAddress
- TCP-based client/server application support
classes: ServerSocket, and InetAddresss
·
Datagram networking
using UDP protocol: DatagramSocket
·
Extension classes:
ContentHandler and URLStreamHandler
Java Sockets
- Provide an interface between a client and a
server
- TCP connection oriented version:
- Java client side socket: Socket class
- Java server side socket: ServerSocket class
- UDP connectionless version: DatagramSocket class
InetAddress Class
- java.net.InetAddress represents an Internet
address class
- Two fields: hostname (a name string), and
address (IP address of integer type)
- Examples of using methods:
import
java.net.*; // class library
InetAddress netaddr1
= InetAddress.getByName(“149.164.36.20”);
InetAddress netaddr2
= InetAddress.getByName(“www.msdn.microsoft.com”);
InetAddress netaddr3 = InetAddress.getByName(“www.microsoft.com “);
InetAddress[]netaddrs = InetAddress.getAllByName(“www.microsoft.com “);
InetAddress
loacladdr = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
If
(netaddrs.equals(netaddr3){action()};
public int
hashCode() .. generate a key for hash
table
public String
toString() .. for passing InetAddress
objects to System.out.println()
InetAddress Programming Examples
1. Examine local host IP address.
// seeLocalIP.java
// 1. Edit the
program
// 2. Microsoft
Visual J++ Compiler and Java Viewer
// C:\jvc seeLocalIp.java
// C:\jview seeLocalIP
// 3. Sun Java JDK
1.22 Complier and Java VM
// C:\javac seeLocalIP.java
// C:\java seeLocalIP.class
//
// RESULTS:
// Dynamic IP
address
//
E:\JavaIASTutorial\DemoProgs\InetAddr>jview e:seeLocalIP
//
default/12.75.199.187
// Different IP address
from the same machine
//
E:\JavaIASTutorial\DemoProgs\InetAddr>jview e:seeLocalIP
//
default/12.75.199.236
import java.net.*;
class seeLocalIP {
public static void main (String args[]) {
try {
InetAddress myIP =
InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(myIP);
}
catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("No IP address
available.");
}
}
}
2. Examine remote server
IP address
//seeIEEEip.java
//
// RESULTS:
//
E:\JavaIASTutorial\DemoProgs\InetAddr>c:\windows\jview e:seeieeeip
//
sphinx5.ieee.org/199.172.136.40
import java.net.*;
class seeIEEEip {
public static void main (String args[]) {
try {
InetAddress readaddr =
InetAddress.getByName("www.ieee.org");
System.out.println(readaddr);
}
catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("Could not find
www.ieee.org");
}
}
}
3. Examine all IP
addresses assigned to a domain name
// seeIEEEips.java
//
// Examine all IP
addresses:
//
sphinx5.ieee.org/199.172.136.40
import java.net.*;
class seeIEEEips {
public static void main (String args[]) {
try {
InetAddress[] addrs =
InetAddress.getAllByName("www.ieee.org");
for (int n = 0; n < addrs.length;
n++) {
System.out.println(addrs[n]);
}
}
catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("Could not find
any www.ieee.org");
}
}
}
HTTP Support Classes
- HTTP servers provide a standard means for
serving and accessing data objects
- On the client side, we need only to use the URL
and/or URLConnection objects to access documents
- Require some extra communication bandwidth than
sockets
URL Class
- java.net.URL is the class for capturing the
abstraction of a uniform resource locator (URL)
- Examples of using methods
- URL includes six fields
- the protocol
- the host
- the port
- the document file
- the URLStreamHandler
- the named anchor or ref
- Methods
- String getFile() .. return the file part of the URL
- String getHost() .. return the host name of the
URL
- int getPort() .. return the port number part of
the URL
- String getProtocol() .. return the protocol
part of the URL
- String getRef() ..return the reference part of
the URL
URL webURL, ftpURL;
URL u = new
URL(“http:www.microsoft.com”);
webURL = new URL(“149.164.36.20”);
URL u = new
URL(“http:www.microsoft.com”);
URL Programming Examples
1. Examine the HTTP and
FTP protocols using URL objects
// ieeeURL.java
//
// This program
examine the URL of the IEEE.
//
// RESULT:
//
http://www.ieee.org/index.html
//
ftp://www.ieee.org/
import java.net.*;
public class ieeeURL
{
public static void main (String args[]) {
URL http_URL, ftp_URL;
try {
http_URL = new
URL("http://www.ieee.org/index.html");
System.out.println(http_URL);
ftp_URL = new
URL("ftp://www.ieee.org");
System.out.println(ftp_URL);
}
catch (MalformedURLException e) {
System.err.println(e);
}
}
}
2. Download a Web Page
(Measurement and Control Server)
//getWebpage.java
//
// This program is executed
from command line. It requires a web
// page address as the
argument. We can display the received page
// on the screen or save it
on the disk using reditection.
//
// The URL.openSteam()
method is used to
// RESULTS:
//
// 1. No arguments were
given
// c:\jview e:getwebpage www.mit.edu
// Exception messgae !!!
// www.mit.edu not a URL
//
java.net.MalformedURLException: no protocol: www.mit.edu
//
// 2. Connection Refused
// C:\WINDOWS>jview
e:getwebpage http://149.164.36.20
//
java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused
//
// Connection OK and display on the screen
// 3. c:\jview
e:getWebpage.class www.mit.edu
// Save it on the disk
// 4. c:\jview
e:getWebpage.class www.mit.edu > mitWpage.html
//
//
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class getWebpage {
public static void main (String args[]) {
URL aURL;
String inBuffer;
if (args.length > 0)
{
try {
aURL = new URL(args[0]);
try {
DataInputStream HTMLpage = new
DataInputStream(aURL.openStream());
try {
while ((inBuffer = HTMLpage.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(inBuffer);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
System.err.println(args[0] + " not a URL");
System.err.println(ex);
}
}
}
}
URLConnection Class
- Communicate directly with a server
- Access everything send by the server in the raw
form (HTNL, plaint text, binary image data, protocol headers in use)
- URLConnection methods in the initialization
phase
- connect
- setAllowUserInteraction
- setContentHandleFactory
- setDefaultUserCaches
- setDefaultAllowUserInteraction
- setDoInput
- setDoOutput
- setIfModifiedSince
- setRequestProperty
- setUseCaches
- URLConnection methods in the connected state
- getAllowUserInteraction
- getDefaultRequestFactory
- getInputStream
- getOutputStream
- getUseCaches
- getDefaultUseCaches
- getDefaultAllowUserInteraction
- getIfModifiedSince
- getDoOutput
- getIfModifiedSince
- URLConnection methods in the idle state
- Applicable methods used in the connected state
- URLConnection parses HTTP header through the
following methods:
getDate()
getExpiration()
getContentLength()
getContentType()
getLastModified()
getContentEncoding()
getHeaderField()
HttpURLConnection Class
- A subclass of URLConnection (new for JDK 1.1 and
up)
- Provide additional HTTP/1.1 specific methods:
GET, POST, PUT, HEAD, TRACE, DELETE, and OPTIONS
- HttpURLConnection Methods:
disconnet()
boolean getFollowRedirects()
String getRequesteMethod()
int getResponseCode()
String getResponseMessage()
getFollowRedirects(boolean)
setRequestMethod(String)
Boolean usingProxy()
JarURLConnection Class
Provide jar-specific methods
for accessing jar-encapsulated date
Networking with Java Sockets
- Provide a stream interface to the TCP protocol
- It will open a Java version of a TCP connection
to the remote host with either a domain name or an IP address
- We can use obtain the information about the
connection through the methods as listed above
java.net.Socket methods
- Socket
- getInputSream() – Get an input stream for the
connection
- getOutputStream() – Get an output stream for the
connection
- close()
-- Disconnect from the remote server
- getLocalPort() – Get the local port number for
the Socket in use
- getPort() – Get the remote port number for the
Socket in use
- getInetAddress() – Get the Internet address for
the connected Socket
A Simple Socket Client Example
1. Create a Socket object for the connection to a remote
server
2. Create an output stream for sending data to the
Socket
3. Create an input stream for receiving data
4. Do Input/Output
5. Close the Socket connection
Networking Servers
- Properties of a server
- Connected to a network continuously
- Wait for a client to connect to it and provide
services
- Has a static network address
- Types of servers:
- Sysnchronous server
- Asynchronous server (background processing)
- Multiclient web server
- States of a server
- Instantiated or constructed
- Accepting clients
- Connected
java.net.ServerSocket
methods
- ServerSocket()
- ServerSocket.accept() – Listen for incoming
connections
- ServerSocket.close() -- No longer listen for new connections
- ServerSocket.getLocalPort() – Get the local port
number for the Socket in use
- ServerSocket.getInetAddress() – Get the Internet
address for the connected Socket
States of a ServerSocket
- Instantiated a new Server Object
- Accepting client connections
- Connected to the remote client
- Close all remote client connections
A Simple Web Server Example
- Initiate the connection to a remote server
- Send/receive data
- Close the connection
Applet
and HTML Documents
Applets
- Properties
- Embedded
in a HTML page
- It sends
by a server for perform client-side application only
- Cannot
be used to build a server from an applet
- Have
limited access to files
- Some
security restrictions
- Can only
make connections back to the host from which they sent
- Cannot
utilized platform-native libraries
- Referring
to host directories
- codebase
– the directory the applet come from
- document
base – the directory that contains the HTML page in which the applet is
embedded
- Other
Class Related Methods
- public
URL getDocumentBase()
- public
URL getCodeBase()
- Applications
- Using
applet for chat application
- Using
applet for downloading data such as images, sounds, etc
Applets Class
- The
Applet class interface and runtime context of the browser/applet viewer
are designed to isolate the code in the Applet from the machine on which
the applet is running
Applet Life Cycle Control
- The Java
system provides methods for controlling the execution of an applet. The
methods as listed below are contained in the class Applet:
- init()
-- initialize the applet each time that it is loaded or unloaded
- start()
-- when the applet is loaded, and begins executing its current task
- stop()
-- when the user leaves the page or exits the browser, the system will
call this method to suspend any outstanding tasks and threads
- destroy()
-- clean up applet before it is unloaded from the browser. All tasks and
threads are halted
A Complete Interactive Applet should be able to
- Read user
input
- Make
decisions
- Uses
arrays
- Perform
output
- Reacts to
the applet life cycle
How
To Create An Applet?
- Create a
project and write Java code in files with .java as an
extension
- Compile
the .java file into byte code with .class extension
- Design an
HTML document that includes a statement to call a compiled Java class
- Open the
HTML document using a Web browser such as Netscape Navigator, Microsoft
Internet Explorer, or an AppletViewer
A Simple Java Applet Example
//HelloWWW.java
// 1.
Edit HelloWWW.java
// 2.
Javac HelloWWW.java
// 3.
Edit HelloWWW.html
// 4.
Use a web browser to view HelloWWW.html
//
import
java.applet.Applet;
import
java.awt.*;
public
class HelloWWW extends Applet {
private int fontSize = 26;
public void init() {
setBackground(Color.black);
setForeground(Color.white);
setFont(new Font("Helvetica",
Font.BOLD, fontSize));
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
g.drawString("Hello, IEEE & World
Wide Web.",
5, fontSize+5);
}
}
<!HelloWWW.html
->
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>HelloWWW: A Simple Applet
Test.</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY
BGCOLOR="YELLO">
<H1>HelloWWW:
A Simple Applet Test.</H1>
<P>
<APPLET
CODE="HelloWWW.class" WIDTH=600 HEIGHT=50>
<B>Error! A Java enabled browser must
be used.</B>
</APPLET>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Ch 5.
Java Native Interface
The Java Platform (a
programming environment)
-
Java Virtual Machine
(JVM)
-
Java Application
Programming Interface (API): a set of predefined classes
The Java
Native Interface (JNI)
- Designed to handle situations where you need to
combine Java applications with native C/C++ native codes
- The needs
- Reuse
C/C++ functions or codes
- Access
system features or devices (such as serial port, digital I/O devices,
etc.)
- Maximize
code execution speed
- Disadvantages
- Losing
program portability
- Two way interface:
- Java à C/C++
- C/C++ à Java
- Support two types of native codes:
- Native libraries
o
Native applications
- Keyword:
- “native” alerts the Java compiler that the
method will be defined externally
- Load C/C++ library code in the run time using
the special loading method. The loadLibrary() located in the
java.lang.System:
void System.loadLibrary(String
libraryName)
- JNI Environment pointer is defined for C
function accessing
Example 1.
Java
Calling printf() function of C’s standard libraries
Step 1. Create a Java file
and compile it (under \jdk\bin directory)
Javac
PrintNative.java
class PrintNative {
publc
native static void greeting();
static
{
System.loadLibrary(“PrintNative”);
}
}
Step 2. Call the javah
utility (under \jdk\bin directory) to produce the following C/C++ header file:
PrintfNative.h
Javah –jni PrintNative
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS
FILE - it is machine generated */
#include
<jni.h>
/* Header for class
Java_PrintNative_greeting */
#ifndef
_Included_PrintNative
#define
_Included_PrintNative
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif
/*
* Class:
PrintNative
* Method:
greeting
* Signature: ()V
*/
JNIEXPORT void
JNICALL PrintNative_greeting
(JNIEnv *, jclass);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
Step 3. Copy function prototype into the following C
program, and prepare some C code.
/* PrintfNative.c
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include
"PrintfNative.h"
JNIEXPORT void
JNICALL Java_HelloNative_greeting
(JNIEnv* env, jclass cl)
{
printf("Hello world!\n");
}
If you use C++ to implement native method, you must declare
that functions are called form Java as extern “C”. The code for C++ is given
below.
/* PrintfNative.cpp
*/
#include
<stdio.h>
#include
"PrintfNative.h"
extern “c”
JNIEXPORT void
JNICALL Java_HelloNative_greeting
(JNIEnv* env, jclass cl)
{
printf("Hello world!\n");
}
4. Compile C program and
make it a Dynamically Loaded Library (DLL)
Option (a) Microsoft C++
compiler, under Windows command:
Cl – IC:\jdk\include
–IC:\jdk\include\win32 –LD PrintNative.c –FePrintNative.dll
Option (b) Under a DOS
virtual machine, set environment path first:
C:\devstudio\vc\bin\vcvars32.bat
Cl – IC:\jdk\include
–IC:\jdk\include\win32 –LD PrintNative.c –FePrintNative.dll
Option (c) Sun Compiler
under Solaries:
Cc –G
–I/usr/local/java/include –I/usr/local/java/include/solaries PrintNative.c –o
libHelloNative.so
5. Compile and run the
following Print.Native.java application to see the string “Hello, World!”
displayed on the terminal screen.
/**
PrintNativeTest.java
*/
class
PrintfNativeTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
PrintNative.greeting();
}
}
Example 2.
Writing a Java
application program that uses Microsoft C function for accessing a
RS232-enabled Radio Shack Digital Multimterer.
Using
JBuilders
set
CLASSPATH=c:\JBUILDER2\lib\jbcl.zip;c:\JBUILDER2\lib\jgl.zip;c:\JBUILDER2\java\lib\classes.zip;c:\java
doskey
c:\jbuilder2\bin\setvars
c:\jbuilder2
/*
*
HardwareInterface.cpp
*/
#include <jni.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "JavaInterface.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <iostream.h>
//#define SIZE 7000
//***************************************************************
// readmm_2.cpp
// Paul I-Hai Lin lin@ipfw.edu
// 8/30/99
//
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Function: CreateFile()
// Opens a file for read and/or write access. It
accepts the name of the file, access
// mode, etc., and returns a handle to the opened
file.
//
// HANDLE CreateFile(
// LPCTSTR
fileName, // File to be opened
//
DWORD accessMode, // Read | Write
// DWORD shareMode,
//
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES security,
//
DWORD create,
//
DWORD attributes,
//
HANDLE templateFile // File containing extended attributes
//
);
//accessMode:
//GENERIC_READ
... Read only
//GENERIC_WRITE
... Write only
//GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_WRITE ... Read/Write
//
//attributes:
//FILE_ATTRIBUTE_ARCHIVE ... mark this as back up file
//FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL ... default
//FILE_ATTRIBUTE_HIDDEN ... mark this as hidden file
//FILE_ATTRIBUTE_READONLY ... mark this as read only file
//FILE_ATTRIBUTE_SYSTEM ... mark this for OS use only file
//FILE_ATTRIBUTE_TEMPORARY ... mark this as
temporary file
//FILE_FLAG_WRITE_THROUGH ... write through cache memory then disk
//FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED
//FILE_FLAG_NO_BUFFERING ... No cache is used as buffer
//FILE_FLAG_RANDOM_ACCESS ... random access
//FILE_FLAG_SEQUENTIAL_SCAN ... sequential access
//FILE_FLAG_DELETE_ON_CLOSE ... delete file when closed
//FILE_FLAG_BACKUP_SEMANTICS ... create a backup file
//FILE_FLAG_POSIX_SEMANTICS ... Follow POSIX naming rules
//
//shareMode:
// 0
... exclusive use of the file
// FILE_SHARE_READ
... read share from the file
// FILE_SHARE_WRITE
... write share file
// FILE_SHARE_READ
| FILE_SHARE_WRITE ... open
access
//
//create:
//CREATE_NEW
... create a new file, it fails if file exits
//CREATE_ALWAYS
... create a new file, destroy old one
//OPEN_EXISTING
... open an existing file, it fails if not found
//OPEN_ALWAYS
... open an existing file, or create a new one
//TRUNCATE_EXISTING
... delete the contents of the file if it exits
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Function: ReadFile()
// Once the file is opened and returned with a valid
file handle, the ReadFile()
// function reads a block of data from it at a time.
//BOOL ReadFile(
// HANDLE file, // created by CreateFile()
// LPVOID buffer, // the buffer for reading bytes
// DWORD requestedBytes, // desired bytes
// LPWORD actualBytes, // actual bytes
// LPOVERLAPPED overlapped
// pointer to overlapped structure
// // for performing background I/O
tasks
// // without necessary multi-threading
// );
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Function: WriteFile()
// Once a file is opened, the WriteFile() function
//BOOL WriteFile(
// HANDLE fileHandle,
// CONST VOID *buffer,
// DWORD byteToWrite,
// LPDWORD bytesWritten,
// LPOVERLAPPED overlap
//
);
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Retrieving the current state of the port
//
//BOOL GetCommState(
// HANDLE
commHandle,
// LPDCB dcb);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Set the current state of the port
//
// BOOL SetCommState(
// HANDLE
commHandle,
// LPDCB dcb);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Sets the timeout values of the port
//
//BOOL SetCommTimeouts(
// HANDLE commHandle,
// LPCOMMTIMEOUTS timeouts); // Time Out Structure
//
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Performs A Specific Operation
//
//BOOL EscapeCommFunction(
// HANDLE
commHandle,
// DWORD operation);
//
// Operations:
// SETDTR Turns
on the DTR line
// CLRDTR Turns
off the DTR line
// SETRTS Turns
on the RTS line
// CLRRTS Turns
off the RTS line
// SETXON Turns
on XON flow control (as though XON received)
// SETXOFF Turns
off XON flow control (as thoigh XOFF received)
// SETBREAK Stops
all transmission until CLRBREAK is received
// CLRBREAK Resumes
tranmission
//
//***************************************************************
//
void ErrorHandler(char *message, DWORD error);
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_JavaInterface_readDMM( JNIEnv *env, jclass obj )
{
HANDLE
comHandle;
BOOL
success;
DCB dcb;
char
str[15];
DWORD
numWrite, numRead;
COMMTIMEOUTS
timeouts;
// Open
the comm port. Can open COM, LPT,
// or
\\\\.\\TELNET
comHandle
= CreateFile("COM1", GENERIC_READ|GENERIC_WRITE,
0,
0, OPEN_EXISTING, FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, 0);
if
(comHandle == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
ErrorHandler("In
CreateFile",GetLastError());
// Get
the current settings of the COMM port
success
= GetCommState(comHandle, &dcb);
if
(!success)
ErrorHandler("In
GetCommState",GetLastError());
// Modify
the baud rate, etc.
dcb.BaudRate
= 1200;
dcb.ByteSize
= 7;
dcb.Parity
= NOPARITY;
dcb.StopBits
= 2; // Two Stop Bit;
dcb.fRtsControl
= 0; // Disable Request to send
// Apply
the new comm port settings
success
= SetCommState(comHandle, &dcb);
if
(!success)
ErrorHandler("In
SetCommState", GetLastError());
//
Change the ReadIntervalTimeout so that
//
ReadFile will return immediately. See
// help
file
timeouts.ReadIntervalTimeout
= 0 ; //MAXDWORD;
timeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutMultiplier
= 0;
timeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutConstant
= 0;
timeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier
= 0;
timeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutConstant
= 0;
SetCommTimeouts(
comHandle, &timeouts );
//while(
x != 5)
//{
//
Set the Data Terminal Ready line
EscapeCommFunction(comHandle,
SETDTR);
//
Send an "D" command to the modem
//
Be sure to use \r rather than \n
strcpy(str,
"D\r");
success
= WriteFile(comHandle, str, strlen(str),&numWrite, 0);
if
(!success)
ErrorHandler("In
WriteFile", GetLastError());
//
Wait 1 seconds and then retrieve from the
//
modem
Sleep(1000);
//
Read 14 characters
success
= ReadFile(comHandle, str, 14, &numRead, 0);
if
(!success)
ErrorHandler("In
ReadFile", GetLastError());
//
Print the string received
//cout
<< numRead << endl;
//str[numRead]='\0';
str[14]
= '\0';
//cout
<< str << endl;
//
//
place a 0 at the end of the character array
//
this is required for the NewStringUTF function
//
//signal[SIZE] = 0 ;
//
//return
the signal buffer to the calling
//java
program.
//
//
Clear the DTR line
EscapeCommFunction(comHandle,
CLRDTR);
//}
CloseHandle(comHandle);
return
(env)->NewStringUTF( str );
}
void ErrorHandler(char *message, DWORD error)
{
cout
<< message << endl;
cout
<< "Error number = " << error << endl;
ExitProcess(1);
}
References
- Java Development Kit (JDK) download site
http://java.sun.com/products/jdk/1.2/index.html
- JNI Books
Essential
JNI Java Native Interface, Rob, Gorgon, 1999, Prenctice Hall, http://www.phptr.com
Ch 6.
Distributed Real-Time Measurement and Control:
A Case Study
Measurement and Control
Server (HTTP server)
- A gateway computer with Flash and RAM memories
(no hard disk)
- A Linux-based HTTP and FTP server
- IP address
- JavaScript (Netscape browser)
- CGI (common gateway interface) program
"gateway_cgi"
- Perform the actual communication between the
embedded devices and the Web
- Designed to receive "field/data"
pairs from a browser via the HTTP POST method
- The "field" is matched to an
identifier in a configuration file
- The "data" string is sent out to the
embedded devices associated with that identifier
- Data from the embedded device is then received
and sent back to the brwoser
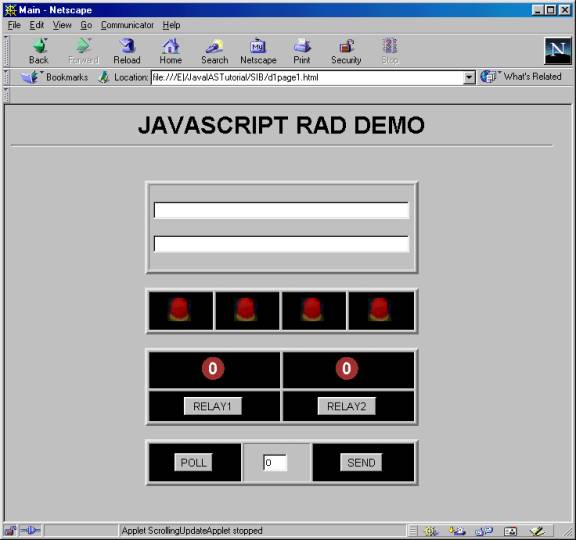
Remote Access Devices
(RAD)
- Serial Port x 1
- Two row LCD display x 1
- Keypad input x 1
- LED output x 4
- Relay outputs x 2
- Opto Input x 1
System Configuration
- Server configuration
- Connect a PC to the server RS232 serial port
- Using Windows Hypertext Terminal program to
login to the server for initial configuration
- Ethernet setting: assign network IP address,
gateway, and subnet mask
- Reboot the system
- Ping the system for testing network connection
- Telnet to system for file editing
- FTP access to upload and download the created
HTML and other needed files
- Remote Access Device (RAD) configuration
- Connect RS232-based RAD devices for digital
Input, digital output, analog input and analog output
- Connect RS485-based RAD devices (up to 4000 ft)
- Clients setup (PC and/or Notebook PC)
- Install Network Interface card, and TCP/IP
protocol
- Assign network IP address, gateway, and subnet
mask
- Prepare HTML pages for control access
Local Network Networking
Access Testing
- A 10/100base hub for connecting the Measurement
and Control Server (HTTP server), PCs, and Notebook PCs
- Same gateway address on all the machines (even
though there is no physical gateway existing)
- Same subnet mask on all the machines
(255.255.255.0)
- Web browser is used as an user interface to the
HTTP server
- On your browser you enter the following command
to access the Measurement and Control Server: http://149.164.36.20
- Trouble shooting:
- Telent (149.164.36.20) to the server and
provide the login password for accessing the system configuration
- IP address verifications
- Update and changes
- Reboot the system
- System shut down
- Telent (149.164.36.20) to the server and
provide the login password for accessing the system configuration
- Shut down
Internet Access Testing
- Setup the Measurement and Control Server (HTTP
server)
- Connect the remote access devices (RAD)
- Web browser is used as an user interface to the
HTTP server
- On your browser you enter the following command
to access the Measurement and Control Server: http://149.164.36.20
Demonstration using
programs provided by Emac, inc (www.emacinc.com)
- expage1.html
- depage1.html
- d1page1.html